
| Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Informatics |


|
Research Spotlight
Omega |
Methods and Algorithms for Parallel Query Processing in Cluster Systems and Grids |
|
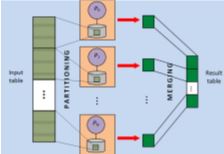
The project is devoted to design and implement a parallel relational DBMS for cluster systems and grids named Omega. The Omega DBMS utilizes the idea of partitioned parallelism where a query is executed by parallel agents run on multiple processor nodes. Each agent processes its own data partition. The distinctive feature of the Omega DBMS is an effective use of many-core node for parallel agent execution. It is reached by utilization of the asynchronous pipeline and bushy parallelism. Keynote papers:
|
PargreSQL |
Parallel DBMS for Clusters on the Basis of PostgreSQL |
|
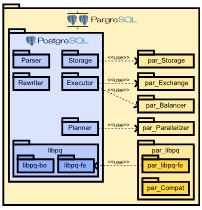
The project is devoted to implement parallel DBMS named PargreSQL based on PostgreSQL opensource DBMS. PargreSQL utilizes the idea of partitioned parallelism and implies modifications in source code of existing PostgreSQL's subsystems as well as implementation of new subsystems to provide parallel processing. Keynote papers:
|
GraphMining |
Mining Very Large Graphs by Means of Parallel Relational DBMS |
|
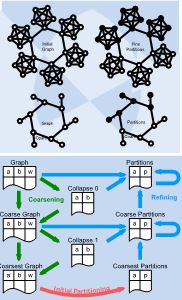
The project is devoted to applying PargreSQL parallel relational DBMS for mining very large graphs, comprising of hundreds of thousands vertices and/or edges. Very large graphs arise in problems connected with modeling of complicated structures, such as circuits, images, chemical compounds, protein structures, biological and social networks, workflows, the Web, etc. The vast majority of existing both serial and parallel algorithms suppose that the graph being mined and all the intermediate data fit into main memory, so they cannot be applied for very large graphs. Keynote papers:
|
Mjolnirr |
Development of private PaaS platform on a basis of hybrid distributed computing system |
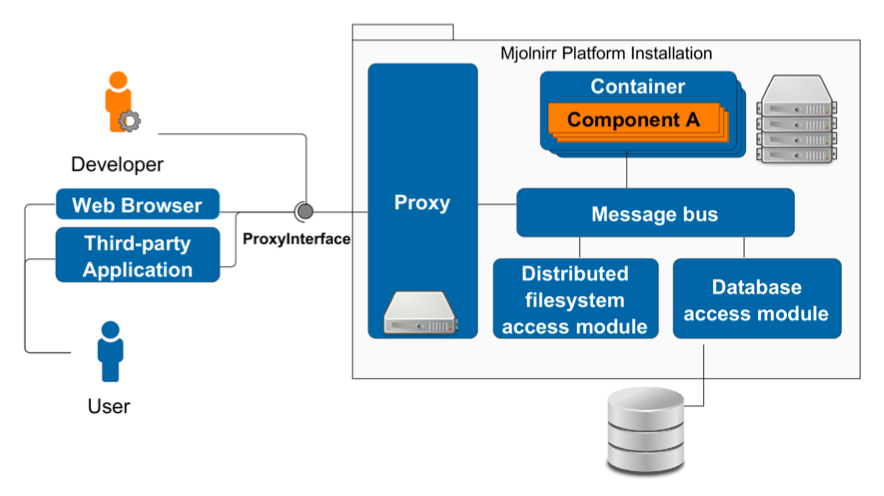 |
The project is devoted to development of private PaaS platform called "Mjolnirr". Any library or Java application can be implemented on the basis of the Mjolnirr platform as a service. From a developer perspective, an application on the basis of the Mjolnirr platform is a set of independent components, which communicate through a message passing interface. Keynote papers:
|
DiVTB |
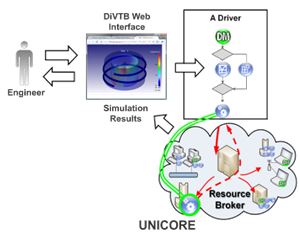
Distributed Virtual Test Bed (DiVTB) |
|
provides a problem oriented approach to access remote distributed supercomputer resources within the grid. DiVTB provides user interface to distributed computing resources, online launch of CAE simulation, automated search, monitoring and allocation of computing resources for carrying out the virtual experiments. The DiVTB Technology provides a solution for DiVTB development and deployment, as well as for CAE system integration into the distributed computing environment (based on the UNICORE grid middleware) and web access to CAE simulation processes. Keynote papers:
|
PVC |
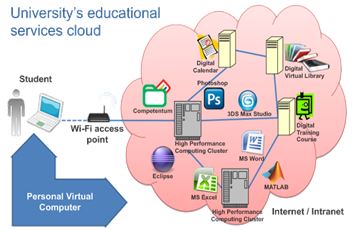
Personal Virtual Computer (PVC) |
|
is the universal way for student to access to the cloud of educational services of the university. The individual PVC (virtual machine) is created on supercomputer for each student with his individual profile. The student may access to his PVC with a computer in laboratory classes, with his laptop, netbook, home PC, tablet, etc. Up to 450 students, teachers and research associates are able to work simultaneously. The total number of users can reach two thousands. |
MedMining |
Mining Very Large Biometric Database of Elite Sportsmen |

|
The project is devoted to discovering set of key performance indicators for elite professional sportsmen by means of mining very large database of their biometric data. Mining results will allow defining and differing profiles of typical, promised and gifted sportsmen and making flexible corrections of their training schedule. The project is carried out in collaboration with scientists from Physical Culture and Sports Faculty of SUSU. |
Urban Heat Island |
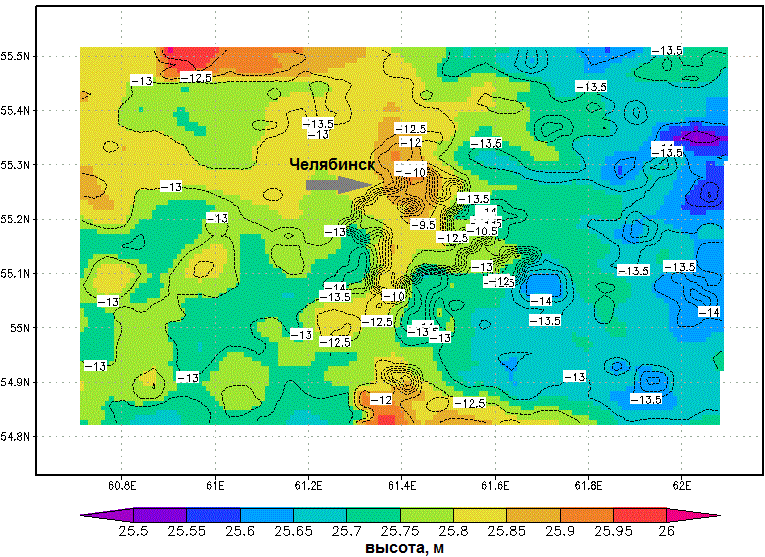
Development of methods for modeling the influence of the structure of agricultural and urbanization on the quality of the environment |
|
Urbanization of territories significantly alters the properties of the underlying surface and the atmosphere (mostly boundary layers) in the local and regional level, which affects the temperature, humidity and wind conditions. The project is aimed at finding methods that combine numerical modeling, field observations and climate database analysis as a geographic information system, which allows the study of various aspects of regional nature in order to protect the public from exposure unfavorable environmental factors. Keynote papers:
|
Analysis and forecast of extreme intensity severe weather events |
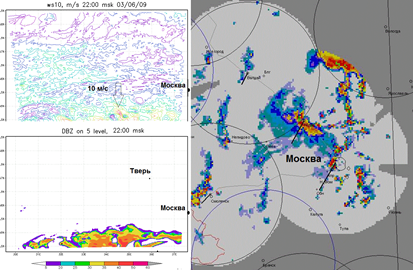
Development of a universal approach to the analysis, the numerical forecast and climatology of mesoscale convective systems and associated extreme intensity severe weather events |
|
The project is aimed at addressing common and regional climatology problems, analysis and forecasting of mesoscale convective systems (MCS), accompanied by a statistically rare extreme weather events (supercells): strong gusts, large hail, tornadoes and very large sums of precipitation (the MCS-supercell). Solution is associated with the development of a universal approach, combining analysis of observations, numerical modeling and climate studies of mesoscale convective systems. It is expected that such methodological platform will predict the occurrence of severe weather events with different lead times and evaluated in relation to the variability of the large-scale circulation conditions and climate trends. Keynote papers:
|
Tel.: +7 (351) 267-90-94
E-mail: vmidek@susu.ac.ru
Website design: Support and Training Department of SUSU SSL


